“In Japanese, Kaizen means “continuous improvement”. “The word implies improvement that involves everyone—both managers and workers”.
Kaizen is for any organisation (manufacturing, process or service) whowishes to improve productivity, reduce costs and improve profitability and establish continuous improvement culture. Kaizen helps to curb waste (MUDA), make operations efficient, relevant and error-free, keep customers satisfied, and eventually improve returns.
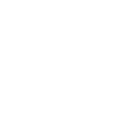
Key Objective of Kaizen is to reduce time line from receipt of confirmed order to the time when the cash in collected by elimination of Non-Value adding (NVA) activities. Any activity that absorbs resources but does not add value to customer or any activity for which customer is not willing to pay for is called NVA or `Muda’.
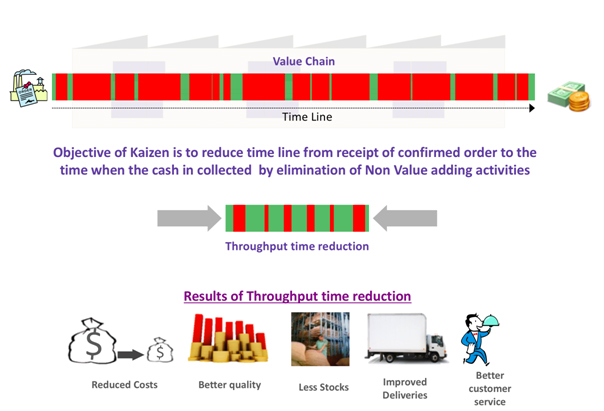
- Over processing – processing beyond customer requirement
Waiting- Operatorssitting idle during machine processing or assembly work
Transportation – unnecessary movement of parts
Inventory – excess raw material, finished goods or semi-finished goods lying in inventory
Motion–excess movement of people
Excess production- producing more or faster than customer requirements
Defects, Rework- rejected goods and high scrap
Non-utilised talent of people–hidden potential capacity or right people doing wrong function
Kaizen aims at improving overall performance of organisation and reducing the cost of operations. Implementing Kaizen with experts can help organisation:
Improving the quality of the work processes results in fewer mistakes, fewer rejects and less rework, shorter lead time, and reduced use of resources.
Kaizen helps organisation to eliminate key issues that impact productivity – reduce waiting time between work processes, material movement between processes, non-value adding activities by employees, manual workflows and imbalanced cycle times. When productivity goes up, cost goes down.
Inventory occupies space, prolongs production lead time, creates transport and storage needs, and eats up financial assets. Kaizen Inventory models helps understand the actual reasons behind inventory gaps & set right levels of production & stock.
A longer production line requires more people, more work-in-process, and a longer lead time leading to much higher cost of operations. Kaizen drives managers to constantly find better ways to do the job than the last time. Implementing Kaizen tools results in better production layout with shorter assembly lines and fewer people to employ.
Kaizen helps minimise machine breakdowns, speed losses & quality losses by using Total Productive Maintenance (TPM), improving Overall equipment effectiveness (OEE)
Kaizen ensures effective Space utilisation & savings through flow management tools like Layout design, cellular manufacturing & Inventory management.
Focus of Lean Kaizen is to continuously reduce Business Throughput time by identifying, reducing and eliminating MUDA (Waste). Eliminating waste along entire value streams, instead of at isolated points, creates processes that need less human effort, less space, less capital, and less time to make products and services at far less costs and with much fewer defects.
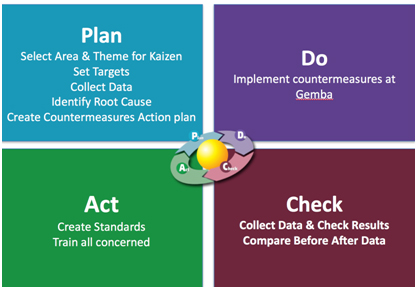
To implement Kaizen successfully and in systematic manner PDCA methodology is used.
: Plan-do-check-act (PDCA) is a cycle which has four stages
Plan:Planning stage covers Identification of key areas for improvement, Setting Targets for improvement, Collect and analyse data thoroughly to understand the problem and identify countermeasures to address the root cause
Do: Implement the countermeasures
Check: Evaluate the results, if targets are not achieved, go back to planning stage to further analyse the problem
Act: Standardize and stabilize the change or begin the cycle again, depending on the results.
One of the most successful ways to implement Kaizen in speedy and systematic manner is through five-day ‘Learn by Doing’ kaizen workshops. Kaizen workshops are also known as Kaizen Blitz, Lean event or Gemba Kaizen workshops. PDCA approach is followed in conducting the Kaizen workshop. After Kaizen projects have been identified, a cross functional team is formed for the project. During the Kaizen workshop, Project team (including staff experts and consultants as well as operators and managers) analyse, implement, test and standardise processes. Kaizen, better known as “the continuous improvement process”, can work wonders when implemented with the help of Kaizen consultants who are experts in process and its application across industries.
During this workshop, various Lean Kaizen tools are implemented to successfully achieve the project objectives. Depending on type of MUDA and losses, different Lean Kaizen tools are used.
5S, a powerful method to improve and sustain workplace organisation. 5S help reduces clutter, reduces the time it takes to look for tools and equipment. Sort, Set in Order, Shine, Standardise and Sustain are key 5 pillars to be implemented. These five pillars results in higher product quality, lower costs, increased customer satisfaction, and corporate growth.
Total Productive Maintenance (TPM) is most successful technique to enhance the reliability, efficiency and productivity of men and machines across an organization. It maximises equipment efficiency, through a system of preventive maintenance, mistake-proofing equipment, to eliminate product defects and to make maintenance easier. TPM not only increases production by improving effectiveness of machines but also helps in increasing employee morale and job satisfaction. The ultimate goal of TPM is zero equipment breakdown and zero product defects, which in turn results in improved utilization of production assets and plant capacity.
Total Flow Management (TFM) is key tool to reduce all types of wastes and is based on principles of Toyota production system and focused on improving of flow of material & information within any organisation. Most of Non-Value adding activities are generated when flow of material or information stops. To improve the material & information flow following are some of the key tools which are used in TFM
Value stream mapping to see waste in material and information flow
- Line balancing: to ensure smooth work flow between processes and individuals
Cellular manufacturing: to improve layout and productivity and throughput
Standard work to ensure best quality and error free work
SMED to reduce changeover times to have smaller batches, thus improve material flow
Pull System to minimise over production and over flow of inventories
Internal logistics flow improvement through Mizusumashi (Water spider) system
External Logistics flow improvement to minimise turnaround time & improve On time In Full Delivery
Total Quality Management (TQM) helps minimise Muda of Defects, Rejection, Rework and aims for Zero Rejection. TQM involves the understanding and implementation of quality management principles and concepts in every aspect of business activities. Total Quality Management demands that the principles of quality management must be applied at every level, every stage and in every department of the organization. The idea of Total Quality Management philosophy must also be enriched by the application of sophisticated quality management techniques.
TQM is a vision which the firm can only achieve through long-term planning, by drawing up and implementing annual quality plans which gradually lead the firm towards the fulfilment of the vision, i.e. to the point where the following definition of TQM becomes a reality:
A corporate culture characterized by increased customer satisfaction through continuous improvements, in which all employees in the firm actively participate. Quality is a part of this definition in that TQM can be said to be the culmination of a hierarchy of quality definitions:
is to continuously satisfy customers’ expectations.
is to achieve quality at low cost.
is to achieve total quality through everybody’s participation.
Several tools under TQM such as 7 QC tools and Statistical process control help curb the defects & rejection.
The key is to engage all employees towards continuous improvement, thereby building Kaizen culture in the organisation. Top Management should plan Gemba Kaizen workshops and training sessions for employees to transform into a Kaizen culture organisation. Companies who implement Kaizen are more open, transparent and innovative.