OEE stands for Overall Equipment Effectiveness. This is different from the efficiency of a machine which is Quantity produced in a certain time.OEE is a factor of the following elements shown below:
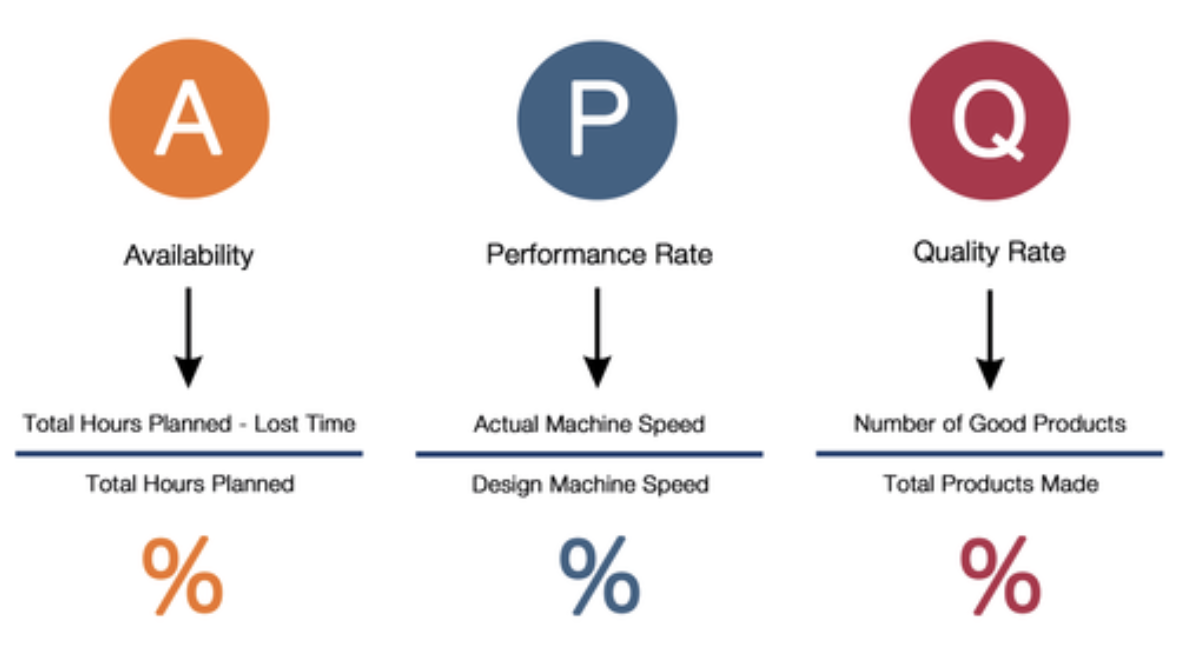
Losses that reduce OEE:
- Losses that Impact Availability –
- Breakdown Loss
- Planned Maintenance Time Loss
- Setup Loss
- Tool Change Loss
- Startup Loss
- Losses that Impact Performance –
- Minor Stoppage Loss
- Reduced Speed Loss
- Losses that Impact Quality –
- Rework Loss
- Defect Loss
TPM Pillars:
- Autonomous Maintenance (Jishu Hozen)
- Planned Maintenance
- Quality Management
- Kobetsu Kaizen
- Health Safety & Environment
- Education & Training
- Office Total Productive Maintenance
- Early Equipment Management
Following Techniques can be used to improve Availability Ratio in OEE:
Major Losses in Availability is #1 due to Breakdown which can be minimized by using following methods based on the Pillars of TPM.
Autonomous Maintenance: We often see Operators sitting idle due to machine breakdown & maintenance teams taking time to visit the site for repair. Hence, creating a departmental mentality of Operator will run the machine & Maintenance team will fix it. In Autonomous Maintenance operator is trained with knowledge & skill on how to keep the equipment from breaking down
Steps to Train the Operator:
- Training on how to clean the equipment every day & inspect
- Basic lubrication routines
- Simple methods to reduce contamination
- Identifying abnormalities before they cause breakdown
- How to repair the machine
Steps to perform Autonomous Maintenance:
- Start with initial cleaning & inspection
- Identify & eliminate sources of contamination
- Set C.L.T.I standard for each equipment(Cleaning, Lubrication, Tightening, Inspection)
- Conduct training
- Conduct random inspection
- Standardization & visual management throughout the shopfloor
- Continuous improvement & updating the standard
Planned Maintenance: Planned Maintenances focuses on Implementation of Time Based Maintenance, Condition Based Maintenance and Predictive Maintenance and is key pillar to be managed by Maintenance team.. This pillar is closely linked with Autonomous Maintenance as Maintenance team is actively involved in training of operators
Steps of Planned Maintenance:
- Equipment condition analysis
- Restoration to basic condition
- Implement information flow system
- Preventive maintenance system
- Predictive maintenance system
Major Losses in Availability is #2 due to Setup Time which can be minimized by using following methods based on the Pillars of TPM.
Focused Improvement (Kobetsu Kaizen): Performing time & motion study of Setup & Breakdown and Applying SMED (Single Minute Exchange of Dies) principle to reduce the down time
Steps of SMED:
- Differentiate Internal & External activities
- Convert internal to External activities
- Streamline all activities
Root Cause Analysis: We tend to find a problem, firefight to solve the problem & the same problem occurs again. This is because we solve only the visible problem & not find the root cause of the problem. Here 5 Why analysis – a simple tool in Root Cause Analysis, plays a huge role in finding the root cause.
If we attack and solve the root cause the chances of recurrence is minimized.
Steps of Root Cause Analysis:
- Pareto Analysis
- Cause & Effect Diagram
- Validation of the above causes
- Why Why Analysis
- Countermeasures
Example of Why Why Analysis-
Visible cause – Machine leakage
Why 1 – Gasket failure
Why 2 – Wear and tear
Why 3 – High vibration
Why 4 – Damaged Bearing
Why 5 – Part not available
Major Losses in Performance Ratio is #1 due to Minor Stoppages which can be minimized by using following methods based on the Pillars of TPM.
Minor Stoppages take place when a machine stops for a brief period of time like 1-2 min until the operator reaches the station and resolves the issue.
Major Causes of Minor Stoppages:
- Misfeeds
- Material Jam
- Obstructed Product Flow
- Incorrect Setting
- Misalignment
- Malfunctioning Sensors
- Equipment design issue
- Lack of cleaning
PM Analysis (Phenomenon Mechanism Analysis) is one of the key tools to reduce Minor Stoppages. When a problem is not as simple to be solved by 5 Why Analysis because the problems are interrelated and complex.
Steps of P-M Analysis:
- Physically analyzing chronic problems: Firstly understand the normal operating condition, then check exactly what is occurring when there is a problem
- Define the problem & the list of causes that is contributing to the abnormality
- Brainstorm & list all possible causes due to 4M (Man, Machine, Material, Method). Eg – Positioning, temperature, machine parameters, raw material
- Measure and compare with standard condition
- If fault found create countermeasures & solve the problem